Many Internet protocols do not prere security, so they are not resistant to eavesdropping, tampering, spoofing, etc.Therefore, VPN technology to increase the security of communication routes is now widely used.Let's take a look at how VPN is used on the Internet. |
VPN that uses the Internet
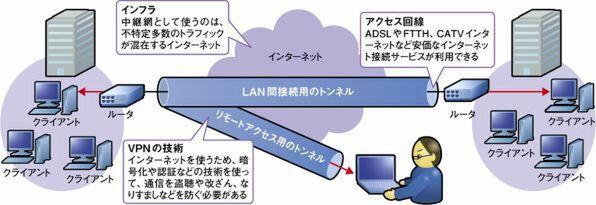
Corporate WAN construction has long been required to have a telecommunications carrier service, including dedicated lines, frame relays, IP-VPN, and wide area Ethernet.However, by using the public network Internet, it is possible for users to build VPN on their own.This is "Internet VPN" (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 Internet VPN built by users on their own
In Internet VPN, tunneling is realized using a VPN -only protocol, and security is ensured.The need for security functions, not just tunning, is behind the Internet.
Unlike the VPN service that uses a closed network of telecommunications carriers, the Internet, which is a mass of multiple networks, is used by many unspecified number of users and has no specific operation manager.Therefore, as described in the series so far, many malicious people may try various security violations.Attacks, fraudulent invasions, eavesdropping and data tampering, fraudulent programs such as viruses and spyware.Therefore, the protocol that realizes Internet VPN offers a security mechanism that opposes eavesdropping, tampering, spoofing.
These VPN protocols include IPsec, PPTP, and SSL.The differences between these VPN protocols are target protocols and operating layers (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 VPN protocols operate.
The target of IPsec is IP, and the IP packet is processed such as encryption and tunning.On the other hand, PPTP is mainly tunneling, authentication, and encryption of Layer 2, not just IP.In addition, SSL is intended for data on the application layer centered on the Web.Due to these differences, each VPN protocol must be used properly depending on the application.
VPN using IPsec
The IP is widely used for communication on the Internet and LAN, but does not provide security.If you capture the packet, the communication content will be completely clear, and you can rewrite the contents on the way.
In response, IPsec complements the security function literally lacking in IP.IPSEC originally made the IPv6 security function used for IPv4 VPN.In addition to tunneling, which is essential for VPN, it has functions such as authentication of communication partners, encryption, authentication, and falsification of IP packets.In recent years, when the application of TCP/IP of applications is spreading, it is the most popular VPN protocol.
The VPN by IPsec is a device called a security gateway. By building a mutual tunnel, VPN communication is possible.In fact, VPN routers and firewalls have VPN functions, and each base and tunnel are built while connecting to the Internet (Photo 1).The VPN router checks the destination of the packet, sends the Internet to the Internet via the ISP, and the packets addressed to the private addresses at the opposite base are treated with VPNs such as tunneling and encryption.In IPsec, such VPNs can be built by using communication modes called "tunnel mode".
Photo 1 Yamaha's VPN router "RTX1100" with IPsec function
The IPSEC tunnel is realized by encapsulating a private address packet to communicate in the LAN with a global address packet used in communication on the Internet.
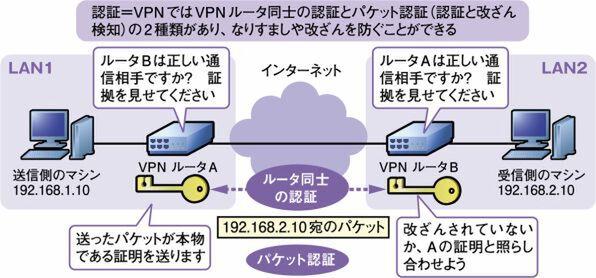
For example, let's look at the case where the Internet VPN is built with LAN1 and LAN2 as shown in Fig. 3.The global address of the destination VPN router B is applied to the original packet so that the LAN1 VPN router can send and receive packets on the Internet when the VPN router A receives a packet addressed to the host from LAN1 to LAN2.The VPN router B of the LAN2 receiving the packet removes the global address header and removes the packet of the original private address.All you have to do is send it to the destination IP address.Both communicating can send and receive packets directly without worrying about going through the Internet.However, this alone does not secure security just by encapsulation of IP with IP.
Figure 3 Tunneling to pass a packet addressed to a private address
そのため、IPsecのトンネルモードでは、ヘッダもユーザーデータもすべて暗号化される。そして暗号化されたIPパケットは「ESP(Encapsulating Security Payload)※1」と呼ばれるIPsec独自の制御パケットでカプセル化される。そして、このESPのパケットに、新しいグローバルアドレスの記載されたヘッダが付与され、インターネットに送信されることになる。一方、受信側のVPNルータでは、ESPのパケットから、IPパケットを取り出し、宛先のプライベートアドレスに向けて送信すればよい。
* 1: ESP ESP performs tunneling, encryption, and authentication, but some countries cannot use encryption technology in private.For this reason, a protocol called AH (Authentication Header), which supports only authentication, is also available.
(Following the next page, following "Certification encryption and authentication / falsification of the communication partner")